HIV tests are crucial tools in combating the spread of HIV. They help individuals know their status, allowing them access to treatment if needed. With advancements in technology, these tests have become more accessible and user-friendly. Today, you can get tested at a clinic, community center, or even do a rapid test at home.
Introduction to the Importance of HIV Testing
Regular HIV testing significantly impacts managing and reducing the spread of HIV. By knowing your status, you can take necessary actions to protect yourself and others. The early detection of HIV allows for prompt medical intervention, which can lead to better health outcomes. Advances in testing mean faster, more accurate results, and tests are more widely available than ever before. These advancements make it easier for people to integrate testing into their regular healthcare routines. Comprehensive testing options cater to different preferences and situations, ensuring that everyone can get tested in a way that suits them best.
Types of HIV Tests: An Overview
Several types of HIV tests exist to meet diverse needs. They vary by detection method, window period, and speed. Knowing these differences helps you choose the best test for you.
Antibody Tests: The Basics
Antibody tests are quite common. They work by identifying antibodies your body produces in response to HIV. These tests can be done using blood or oral fluid samples. Usually, antibodies develop within 23 to 90 days after exposure. Because of this window period, if you’re worried about recent exposure, retesting may be necessary. They are popular because they can be done quickly and are available both in clinics and at home as HIV rapid tests.
Antigen/Antibody Tests: Improved Detection
These tests detect both antigens and antibodies, allowing for faster detection of HIV. They generally show results sooner than antibody tests, with a window period of 18 to 45 days. This makes them a great option for people who suspect recent exposure. Laboratory tests tend to be more precise, but HIV rapid tests offer quick results in non-lab settings. These tests are a balance between speed and accuracy.
Nucleic Acid Tests (NAT): Early Detection
Nucleic acid tests, or NATs, detect the virus itself, rather than the antibodies or antigens. This makes them incredibly effective at early detection, with a short window period. NATs are ideal for recent exposures or evaluating early symptoms. These tests are often more costly and complex, usually performed in labs. They can also assess viral load, crucial for planning treatments.
The HIV Test Procedure: What to Expect
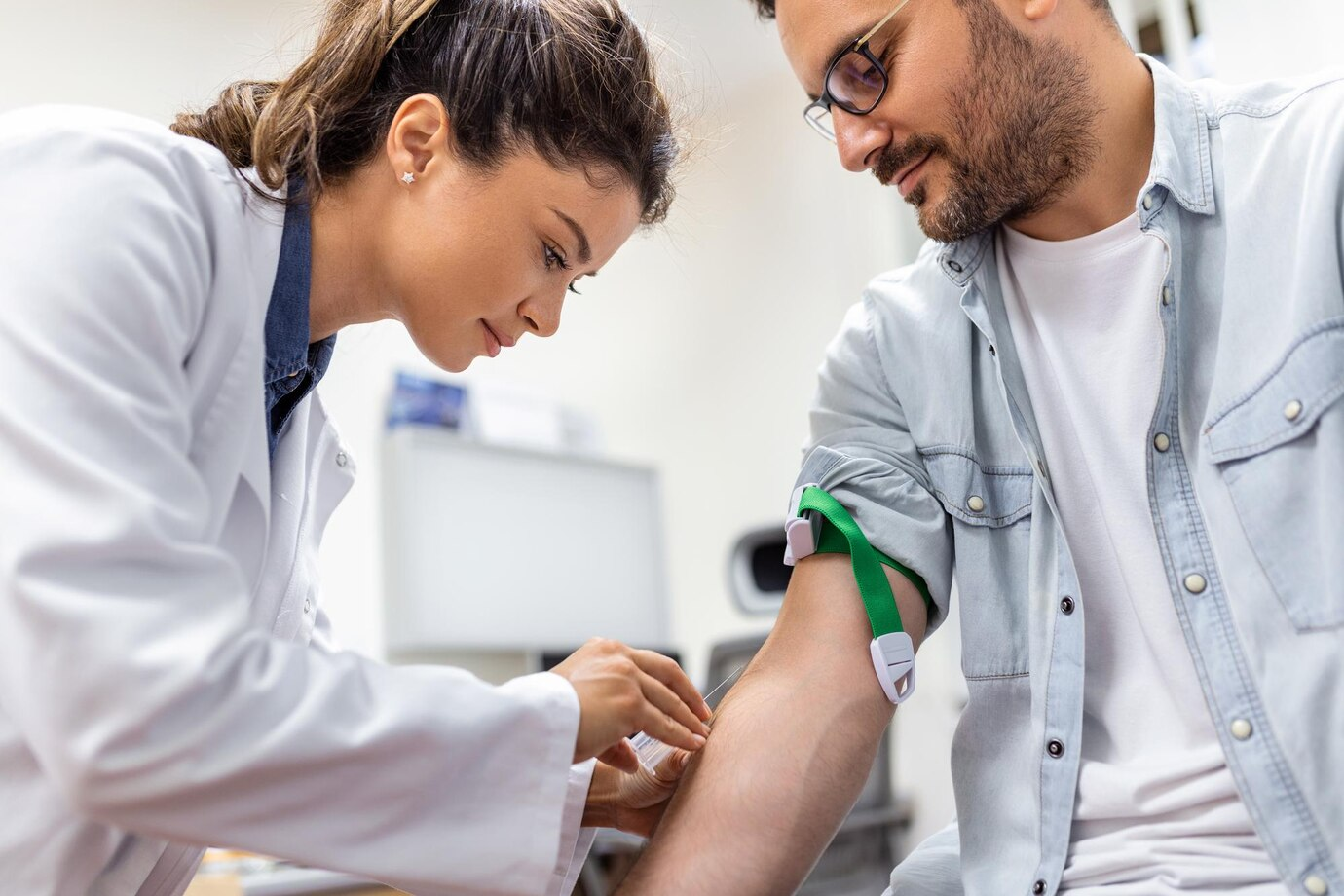
Tests generally involve a sample of blood, oral fluid, or urine. The HIV test procedure is straightforward and often quick. You might get immediate results or wait a few days for more detailed analysis.
Blood-Based Testing: Accuracy and Process
Blood-based tests involve either a vein blood draw or a finger stick for quicker results. They are known for their accuracy, with the window period varying depending on the test type. Though blood draws are more thorough, HIV rapid tests from finger sticks offer immediate answers. This quick process is both convenient and effective.
Alternative Testing Methods
For those wary of needles, there are alternatives like oral fluid and urine tests. These methods are easy and painless but might have different accuracy levels compared to blood tests. You trade some precision for comfort. Alternative methods allow more people to get tested without stress.
Understanding Your Results
Getting results can be nerve-wracking. However, understanding them is straightforward. Whether your results are negative or positive, knowing your next steps is key.
Negative Results: Next Steps
A negative result means no detection of HIV at this time. Keep in mind the window period; retesting might be smart if exposure was recent. Embrace preventive practices like safe sex and regular testing. Consider ongoing screening as an integral part of your health routine.
Positive Results: Immediate Actions
A positive result requires follow-up with a healthcare provider for confirmation. Immediately connect with medical care for support and know that various resources are available. From counseling to treatment plans, there is comprehensive help available to manage your health effectively.
Accessibility: Where to Get Tested
Accessibility to HIV tests is essential. Testing options in healthcare facilities, community centers, and at home make it easy.
Healthcare and Community Testing Locations
Hospitals and clinics provide structured, trusted testing environments. Community centers often offer free or low-cost options, making them accessible to everyone. Mobile testing services increase reach, bringing the test to your location.
Home Testing: Privacy and Convenience
Home tests offer privacy, allowing you to manage testing yourself. FDA-approved kits, including HIV rapid tests, let you test confidently. Mail-in options give the convenience of home collection with lab accuracy. This privacy can make all the difference.
Conclusion: Encouragement to Act
Regular HIV testing empowers you to take control of your health. It’s as normal as any routine check-up and is critical for preventing the spread of HIV. Understanding that knowledge is power, embrace testing as part of your healthcare habits. Encourage yourself and others to prioritize HIV tests as part of a healthy lifestyle.